Graded Potential And Action Potential Animation
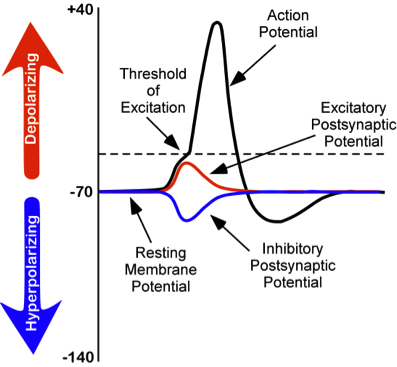
Epsps are caused by a hyperpolarization of the post synaptic membrane.

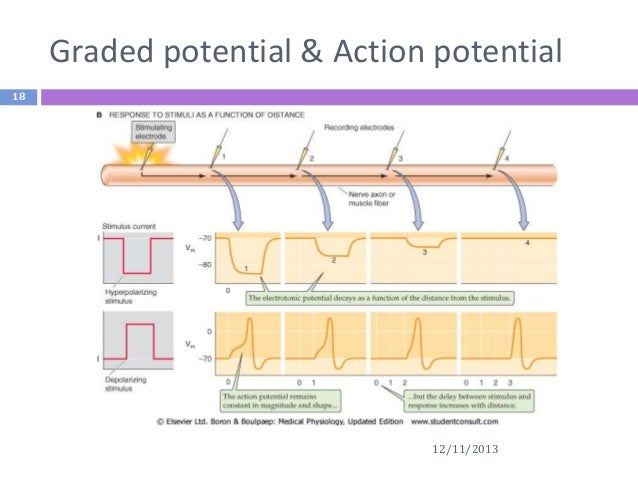
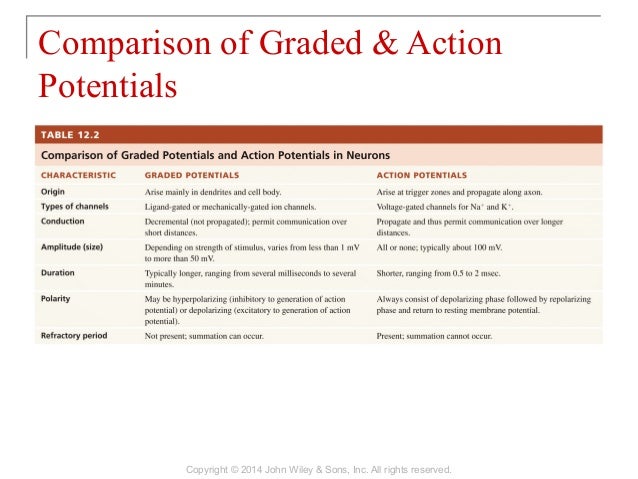
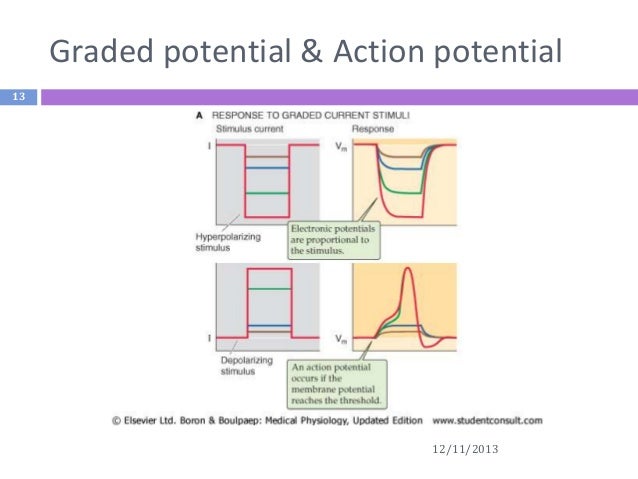
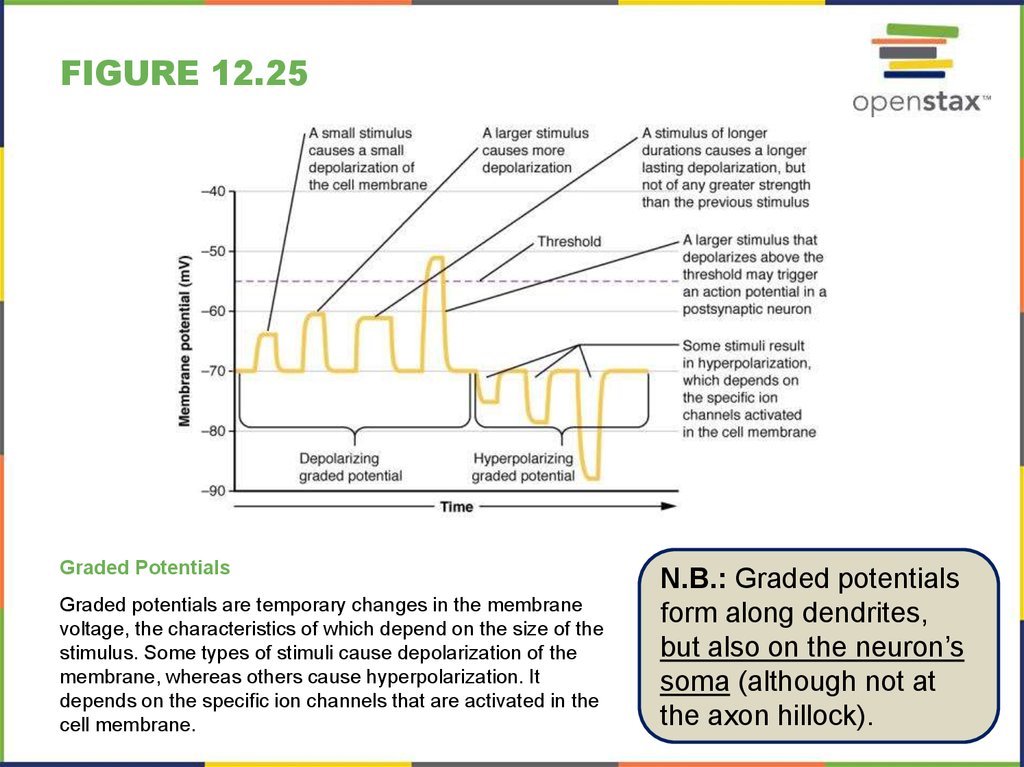
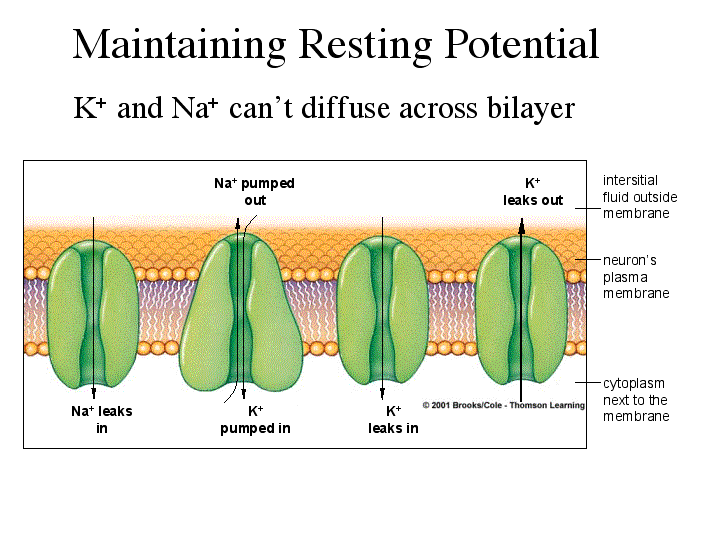
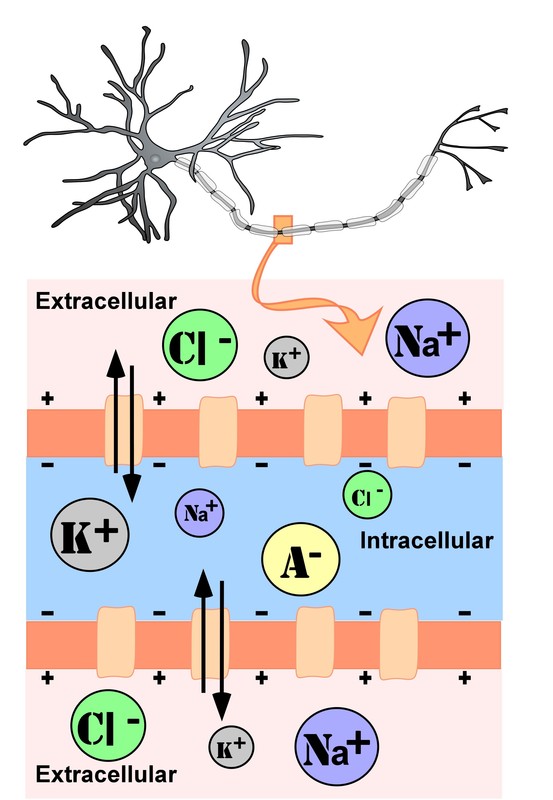
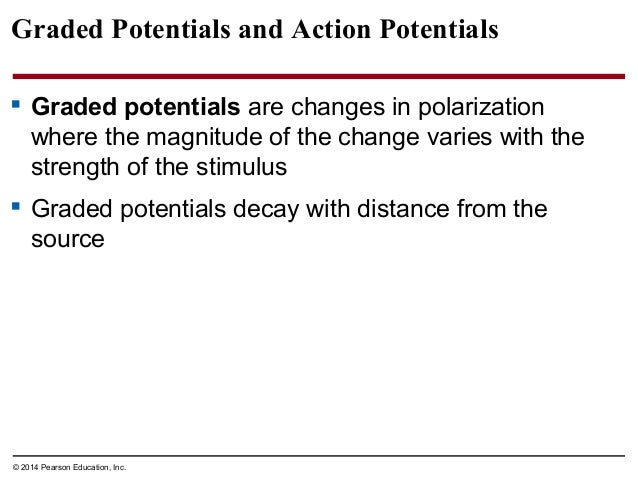
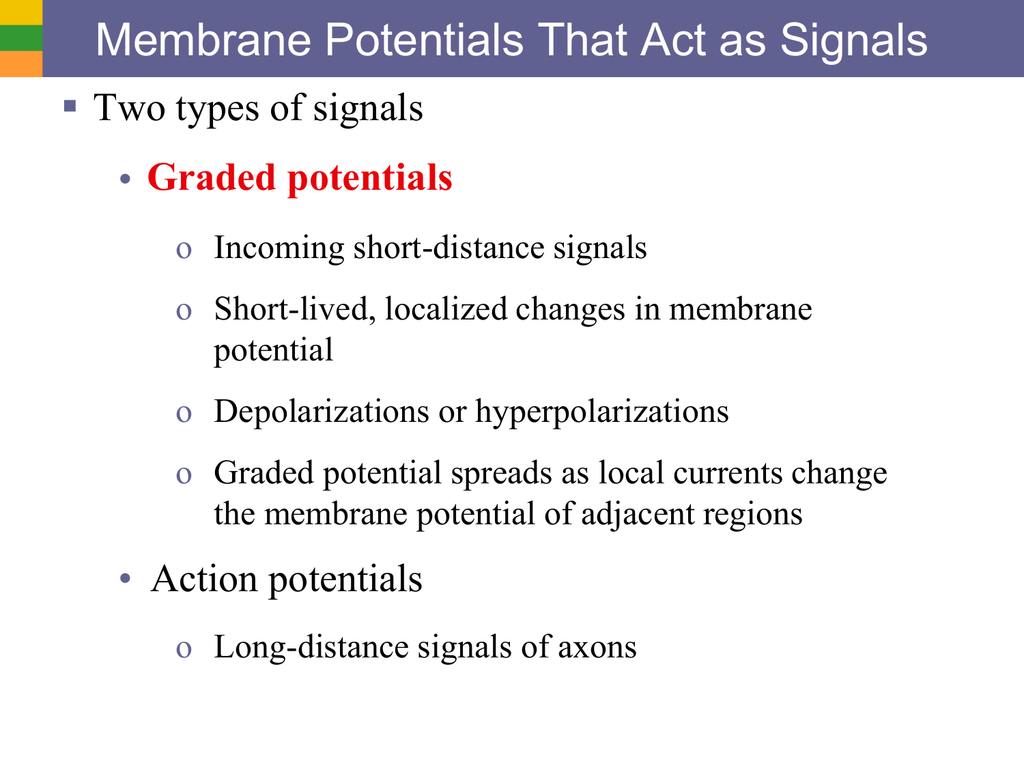
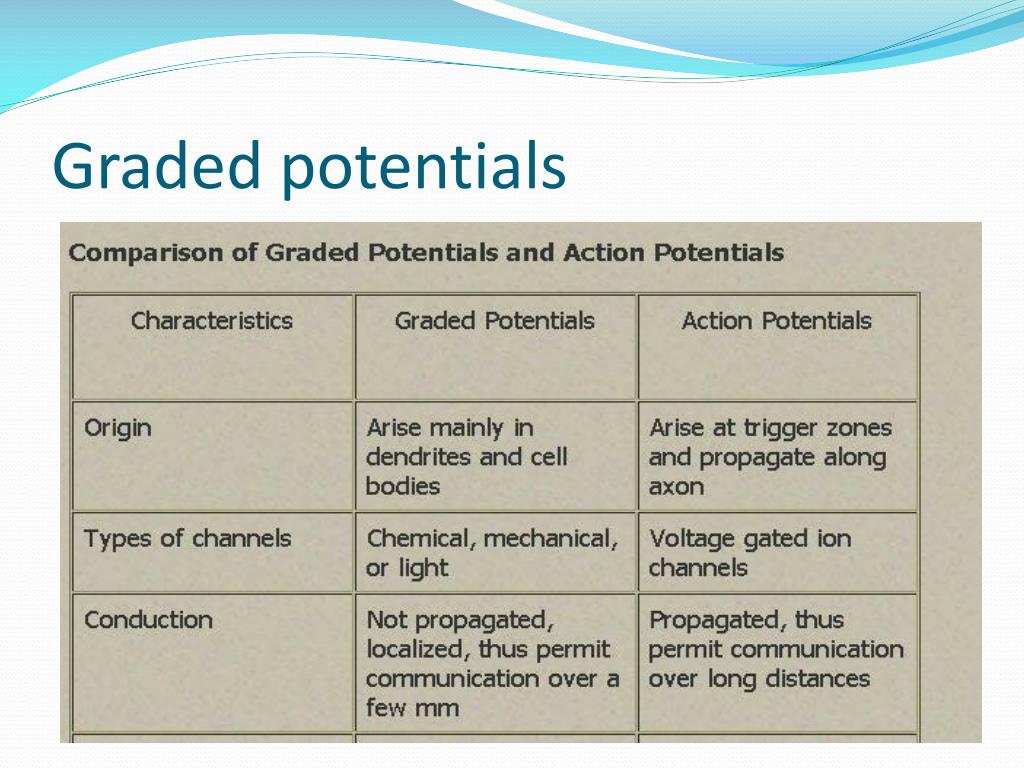
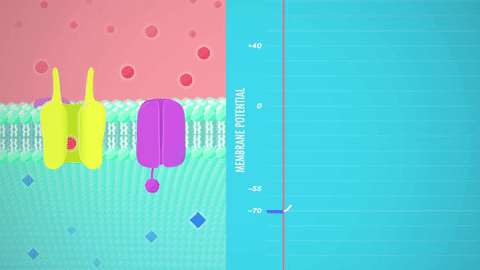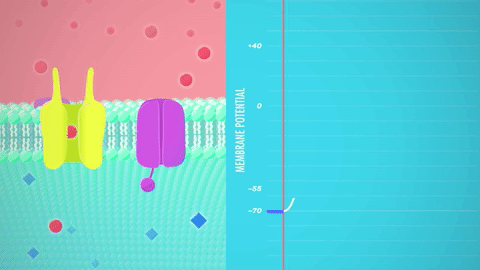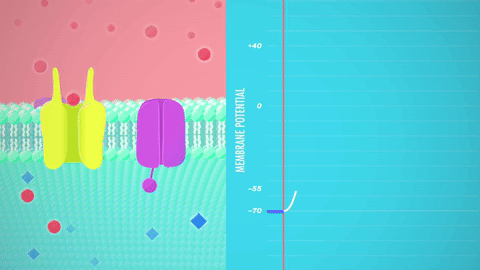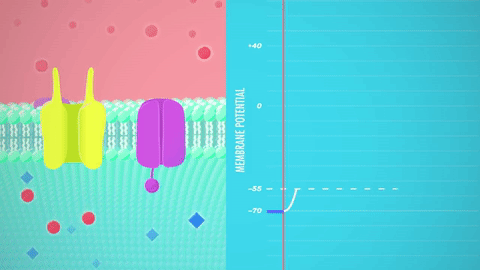
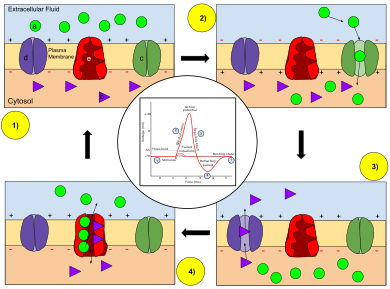
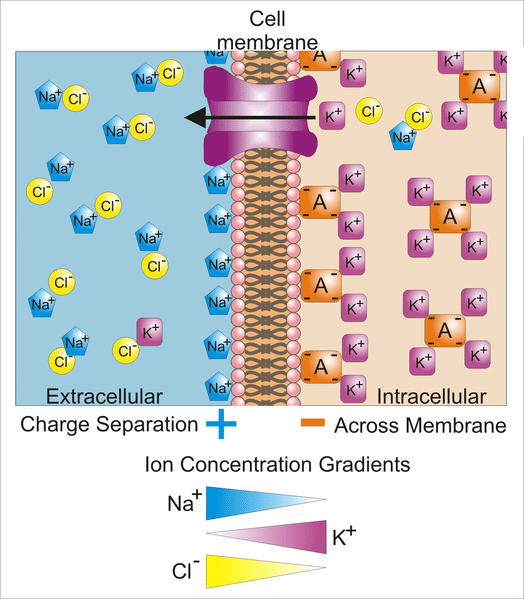
Graded potential and action potential animation. All the body cells show membrane potential largely due to the uneven distribution of sodium chloride and potassium ions and also due to the permeability difference of the plasma membrane to these ions. The mechanism of muscle contraction. The main difference between graded potential and action potential is that graded potentials are the variable strength signals that can be transmitted over short distances whereas action potentials are large depolarizations that can be transmitted over long distances. Graded potential vs action potential.
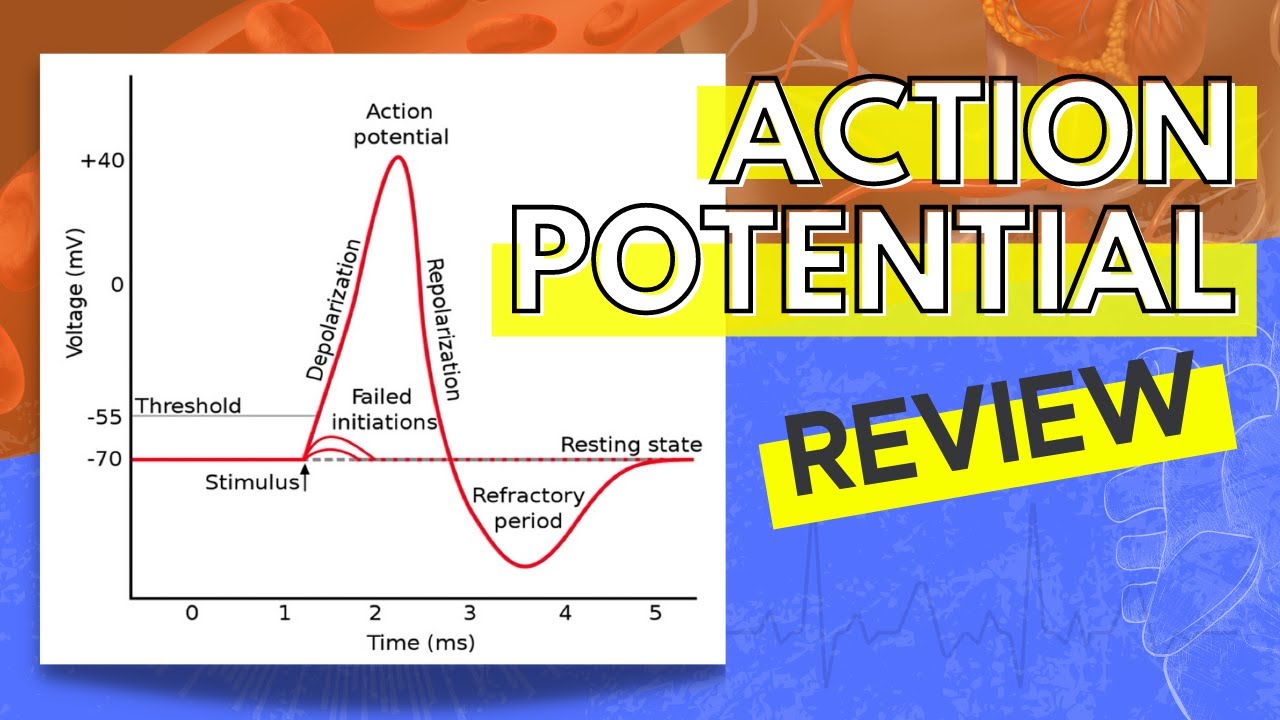
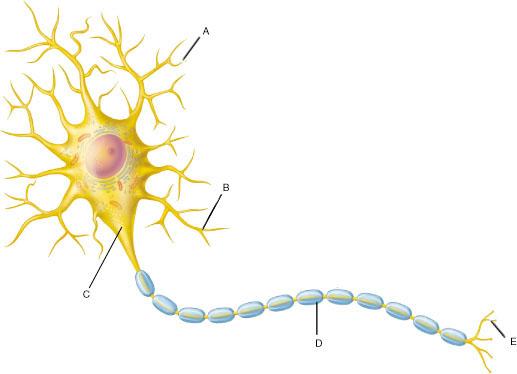
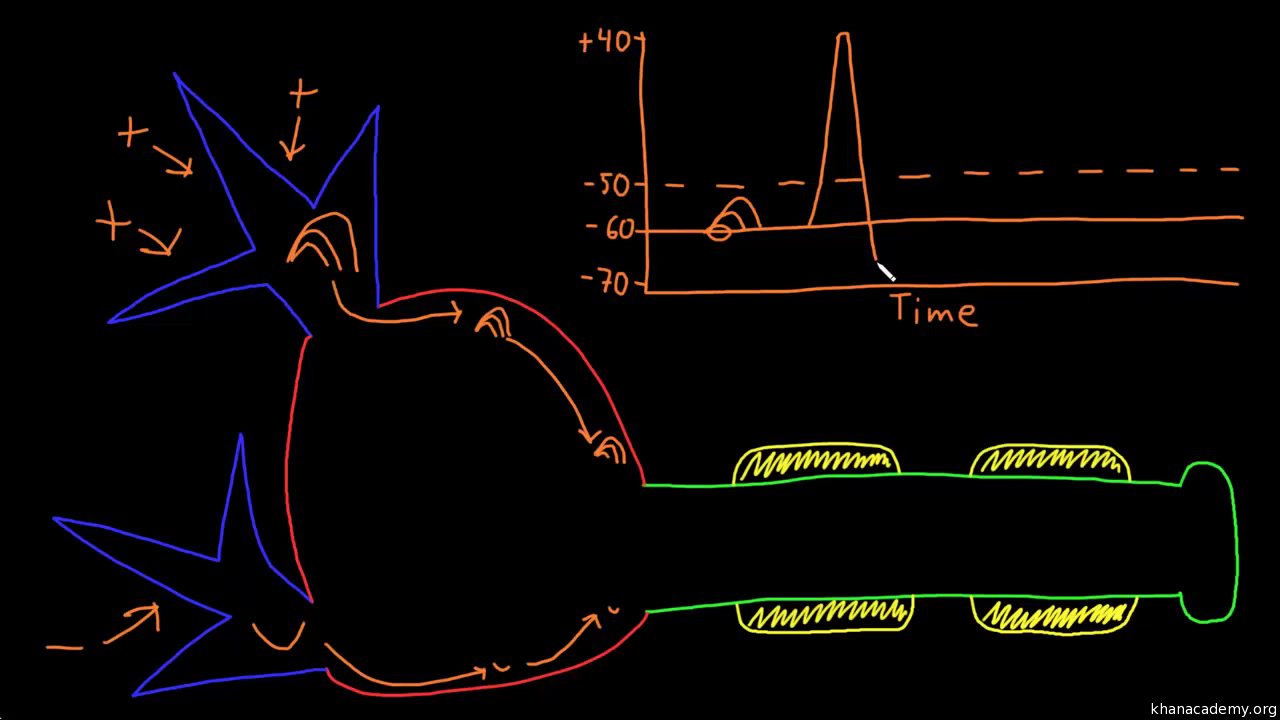
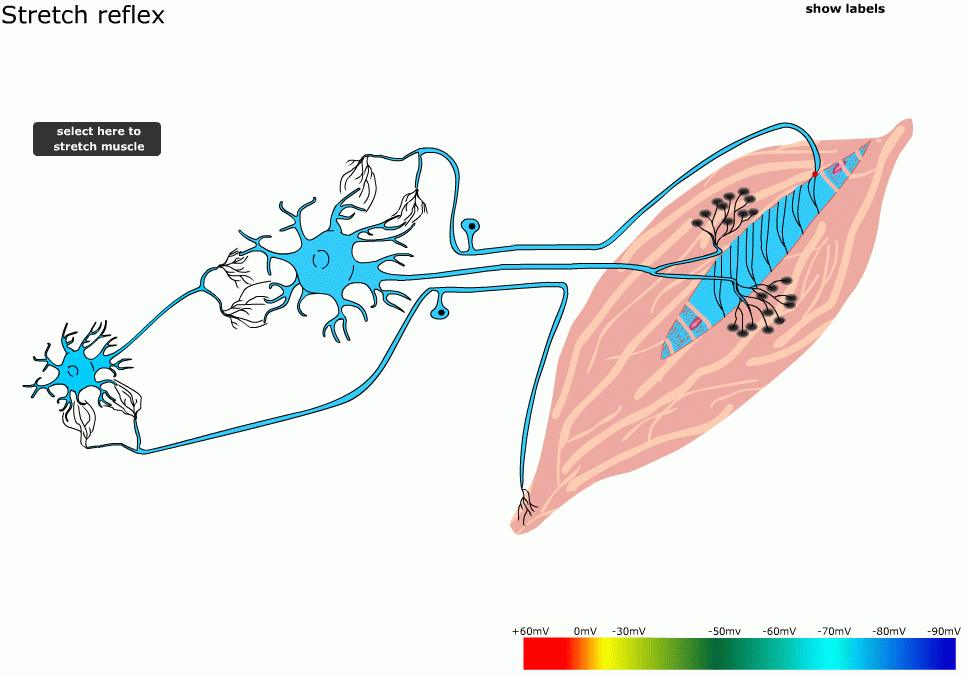
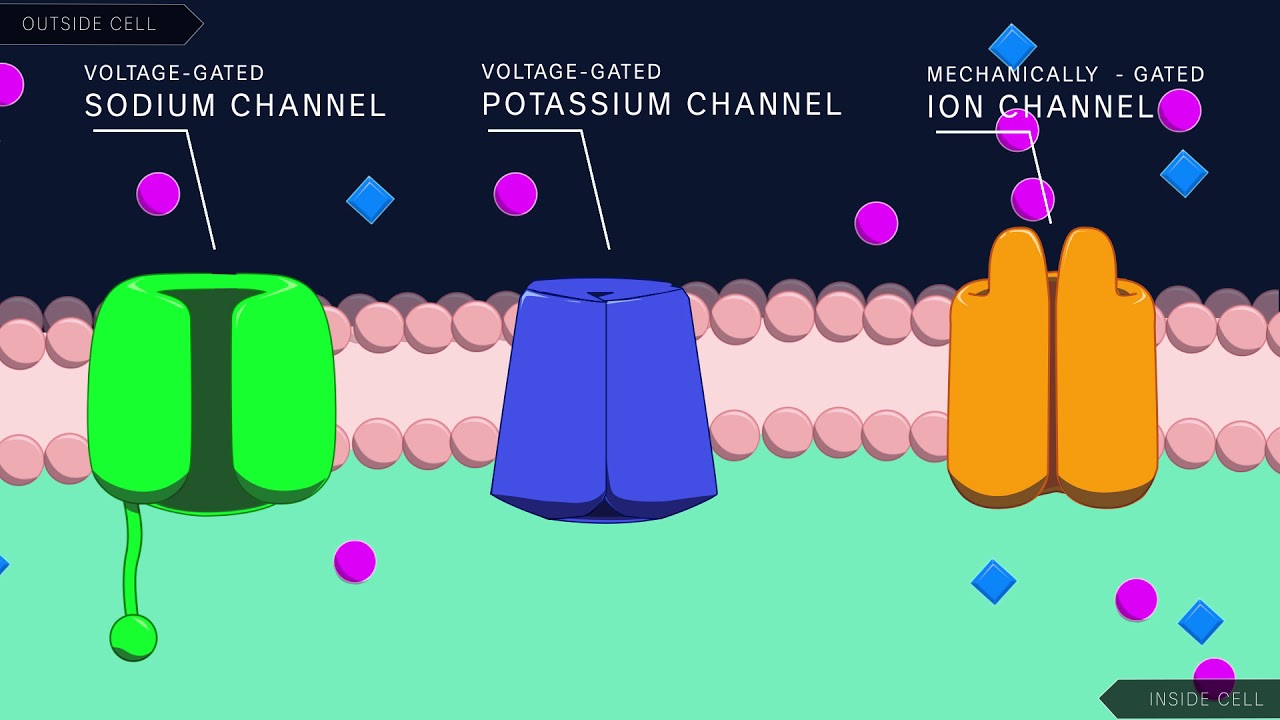
Neuron action potential mechanism. Differentiate between resting graded and action potential with reference to structures of the neuron as well as ion movements and membrane potentials. An action potential ap is the mode through which a neuron transports electrical signals. Graded potentials will typically generate an action potential.
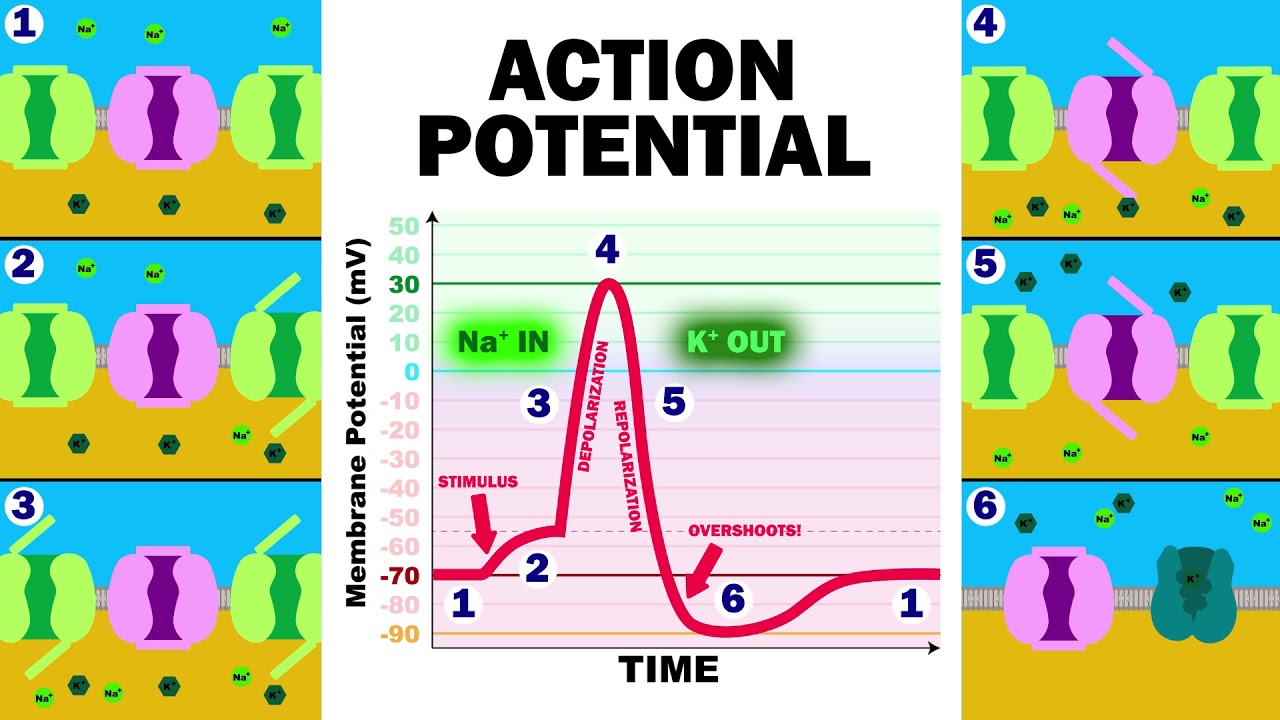
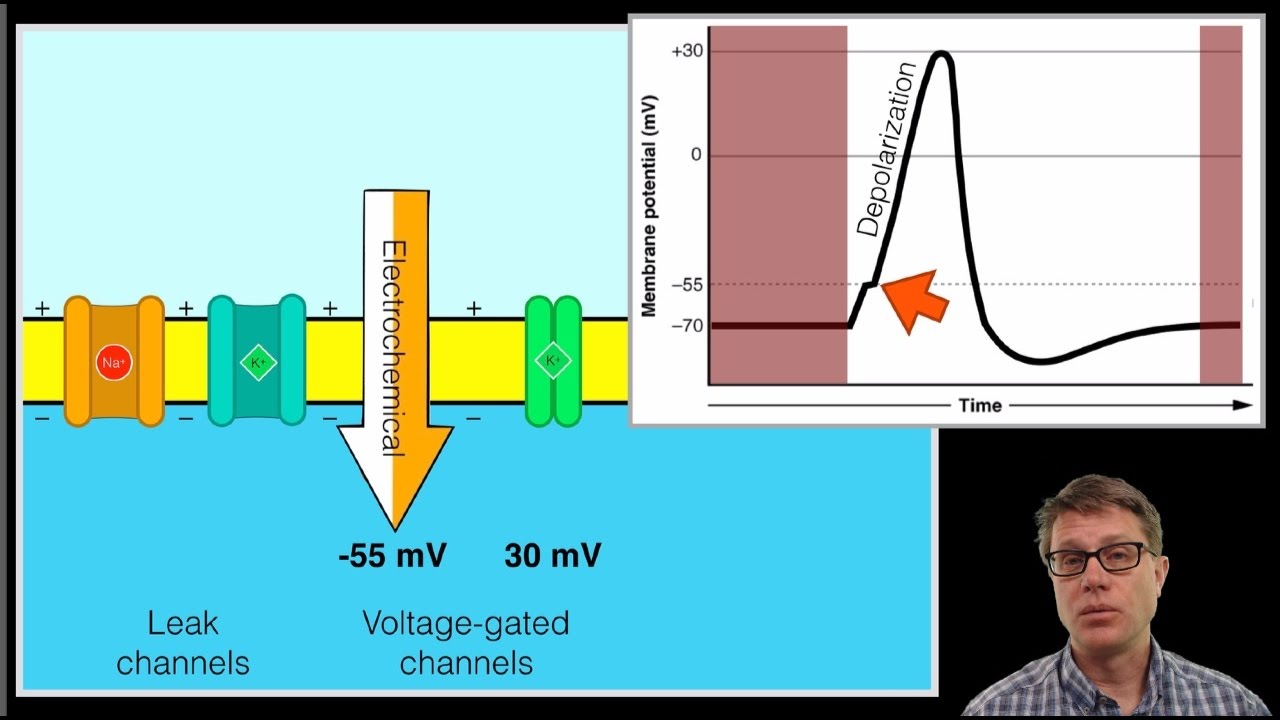
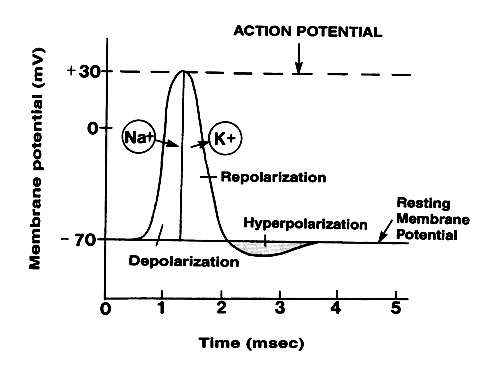
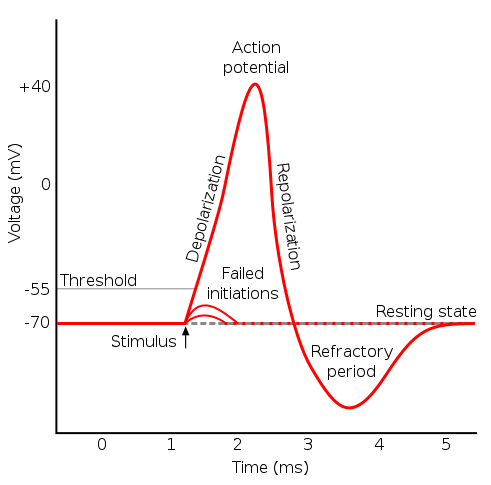
Neuron graded potential mechanism. Neuron action potential description. It is defined as a brief change in the voltage across the membrane due to the flow of certain ions into and out of the neuron. In this article we will discuss how an action potential is generated and how conduction of an action potential occurs.
And also the voltage. This is the currently selected item. Start studying chapter 12 animation. Graded potential action potential duration.
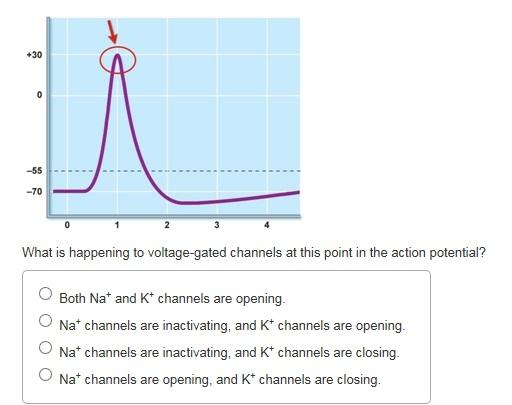
Sarcomeres action potential and the neuromuscular junction duration. A voltage gated potassium channel also plays an important role in increasing the rapidity of repolarization of the membrane. This membrane potential results in positive and negative charges across the membrane. The mechanism of muscle contraction.
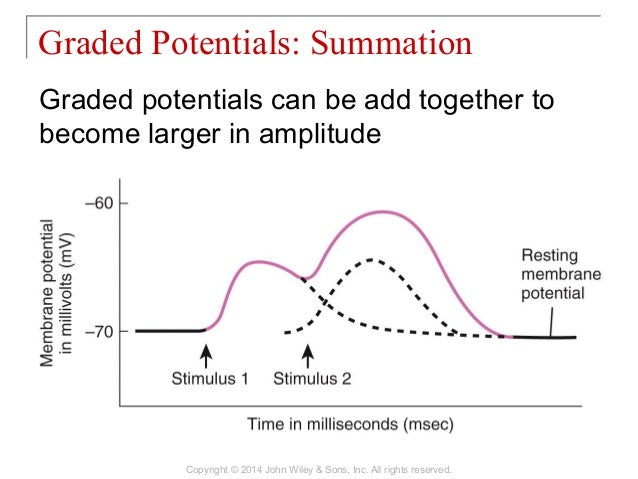
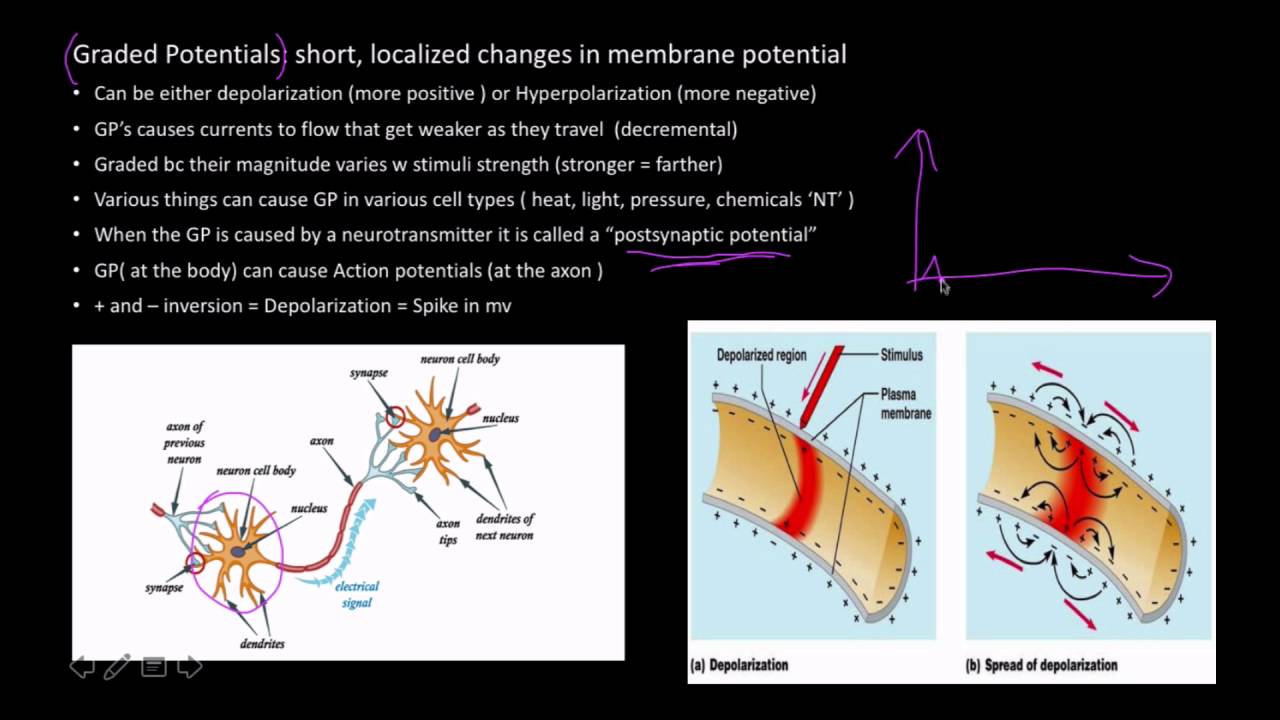
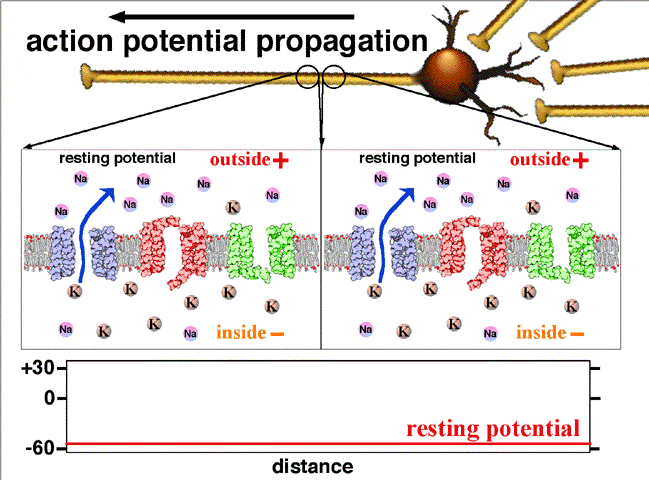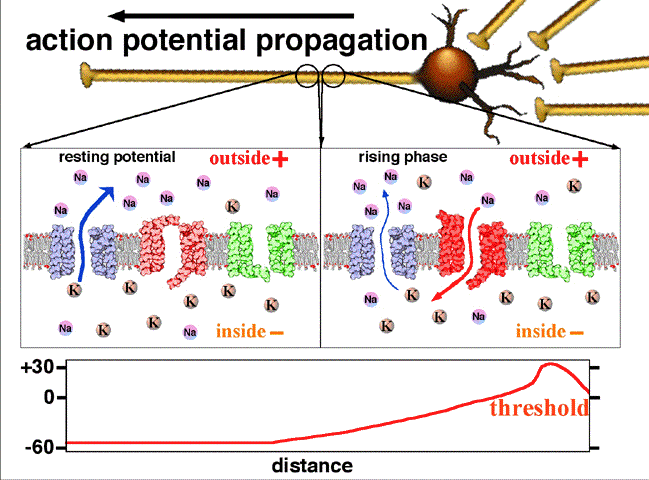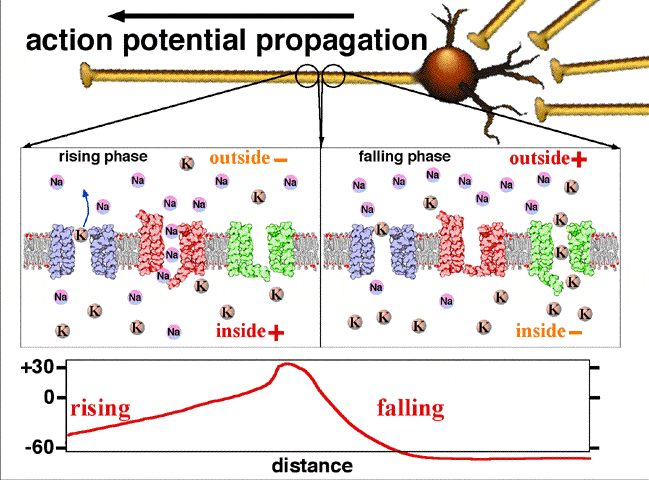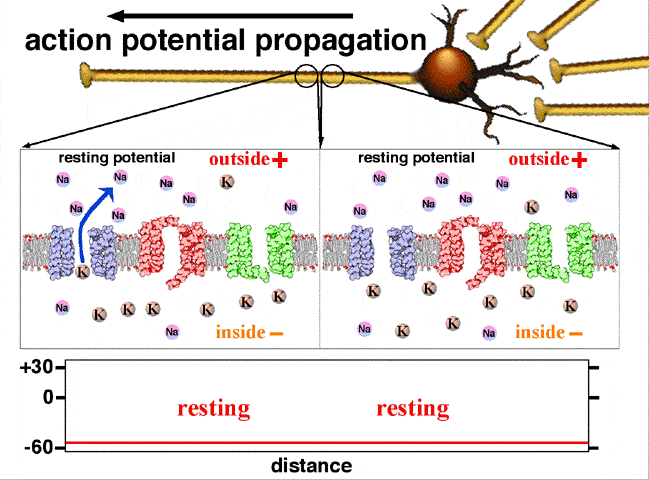
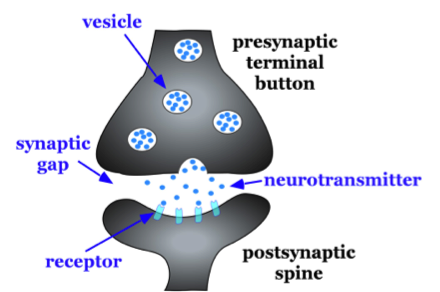
Graded potential and action potential are the two types of potential differences that can be generated during depolarization. Unlike graded potentials the propogation of an action potential is unidirectional because the absolute refractory period prevents the initiation of an ap in a region of membrane that has just produced an apin myelinated axons aps appear to jump from node to node in a process called saltatory conduction because no depolarization occurs between the nodes. And then the action potential stops falling because now its more negative inside the neuron again so theres less driving force pushing potassium out through the leak channels. Events at the synapse.
Anatomy and physiology for paramedics 24394 views. The nervous system of the common laboratory fly drosophila melanogaster contains around 100000 neurons the same number as a lobster. This number compares to 75 million in the mouse and 300. Professor dave explains 190516 views.